Llega el final del curso y con él los alumnos de STI han presentado sus proyectos. Carlos y Eneko nos hablan del increible mundo de las criptomonedas, el cual día a día es más conocido e importante.
Estos dos alumnos han decidido montar una granja de criptomonedas? Pero de qué estamos hablando exactamente?

Diferentes Criptomonedas.
Casi todos hemos oído hablar del famoso Bitcoin, pero la gran mayoría de las cosas que escuchamos son historias de gente convirtiéndose millonaria y precios muy disparados. Bueno, en si el Bitcoin es una criptomonedas, pero como ella existen muchas más (pj. Ethereum, LTC, XMR, DogeCoin, etc..), las criptomonedas son un sistema de intercambio digital, pero a diferencia de cualquier otra divisa que conocemos, no está respaldada por un gobierno o un país.
Mucha gente se pregunta si son seguras, y la respuesta es que si, y esto es por cómo funcionan. Explicado de forma muy sencilla (ya que el tema es bastante complejo) las criptomonedas se crean cuando son minadas. Pero qué es minar? En qué consiste? Bien, minar es cuando una persona (el considerado minero) tiene una computadora dedicada a validar transacciones de otros usuarios, esto se hace mediante la aplicación de firmas criptográficas en cada bloque de transacciones, estas deben cumplir ciertas condiciones mediante una proof-of-work que traducido significa prueba de trabajo, y nuestra computadora lo que está haciendo internamente es resolver una función criptográfica con los valores del bloque en cuestión y otro valor aleatorio, cuando nuestra computadora resuelve esa función satisfactoriamente, es decir su resultado cumple con la condición puesta, se nos premia con una cantidad de esa moneda, por lo que se generan nuevas unidades. Los valores usados en las funciones se encuentran en los bloques, y cuando se resuelve uno de esos bloques, otra persona comprueba que es correcto y así sucesivamente, de esta forma las comprobaciones se van apilando una detrás de otra, formando lo que conocemos como la blockchain, que es un archivo donde se quedan guardados todos los movimientos, y todo el mundo tiene una copia de ese archivo. Hay gente que piensa, y qué pasaría si yo doy comprobaciones falsas una y otra vez, el sistema no funcionaria, se harían transacciones falsas y encima me premiaron por ello? Si, pero a la vez que tu, hay otros millones de mineros realizando esas comprobaciones, y tendrias que tener más del 50% de las computadoras del mundo para poder hacer eso, por lo cual es casi imposible que alguien rompa el sistema. Esto es a lo que se llama tener un sistema descentralizado, es lo que hace el sistema totalmente transparente y seguro.
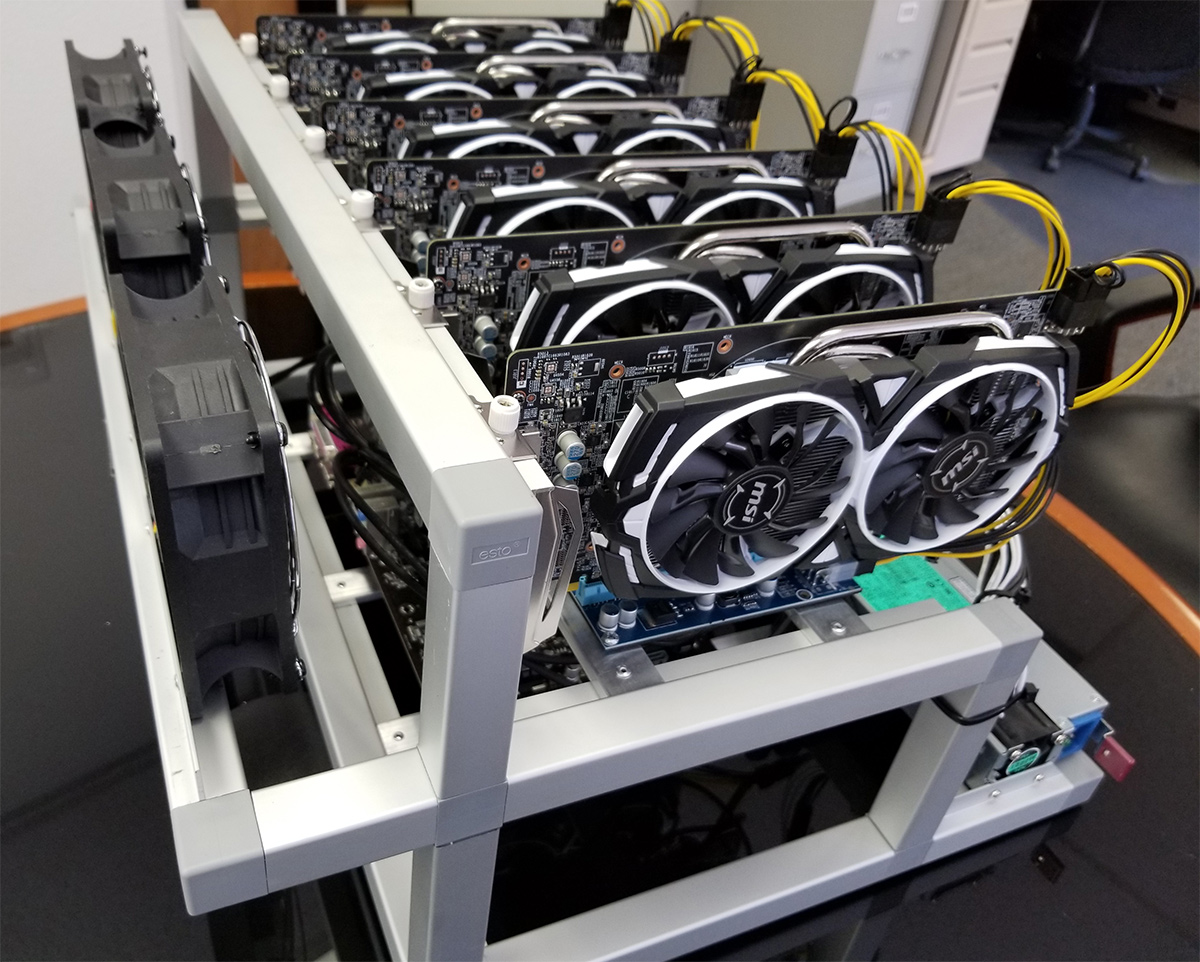

RIG de mineria
Lo que ocurre, es que resolver estas funciones criptográficas y encontrar (al azar) un valor que al aplicarlo en la función cumpla ciertos requisitos, es muy complicado hasta para un ordenador, por lo que se utilizan computadoras dedicadas, que son conocidas como RIGs de minería. No obstante aunque dispongamos de un RIG, nos resultará muy complicado resolver una de estas funciones criptográficas solos, por lo que los mineros se juntan en las denominadas “pools de minería” para repartirse el trabajo entre ellos y después repartirse el beneficio.
Nuestro proyecto se basa en montar muchos RIGs y monitorizar los RIGs para que no tengamos que estar pendientes de ellos, y sean lo más autosuficientes posibles, Si mañana 29 de Mayo os pasáis por el aula de STI tendréis la oportunidad de ver nuestra exposición del proyecto donde explicaremos todo esto en detalle y mucho más!
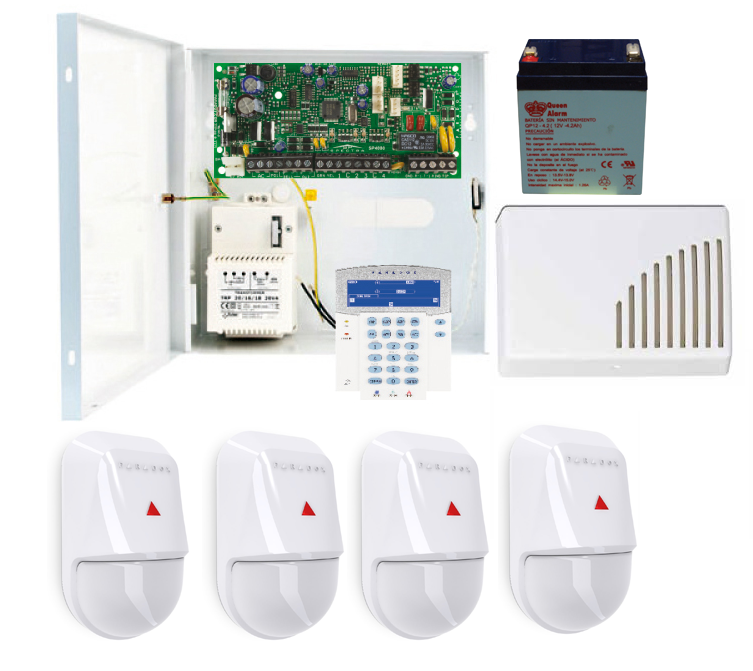
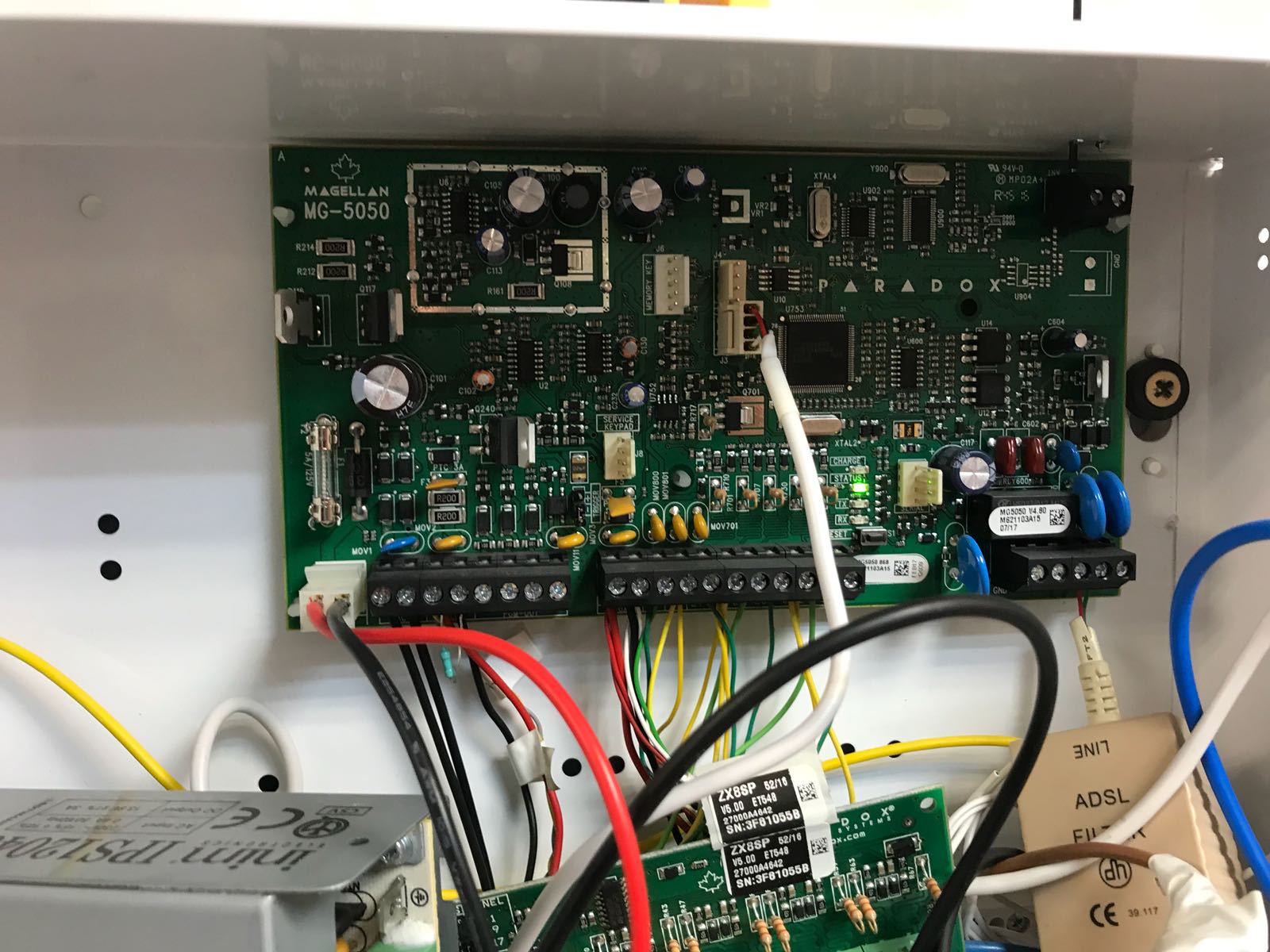
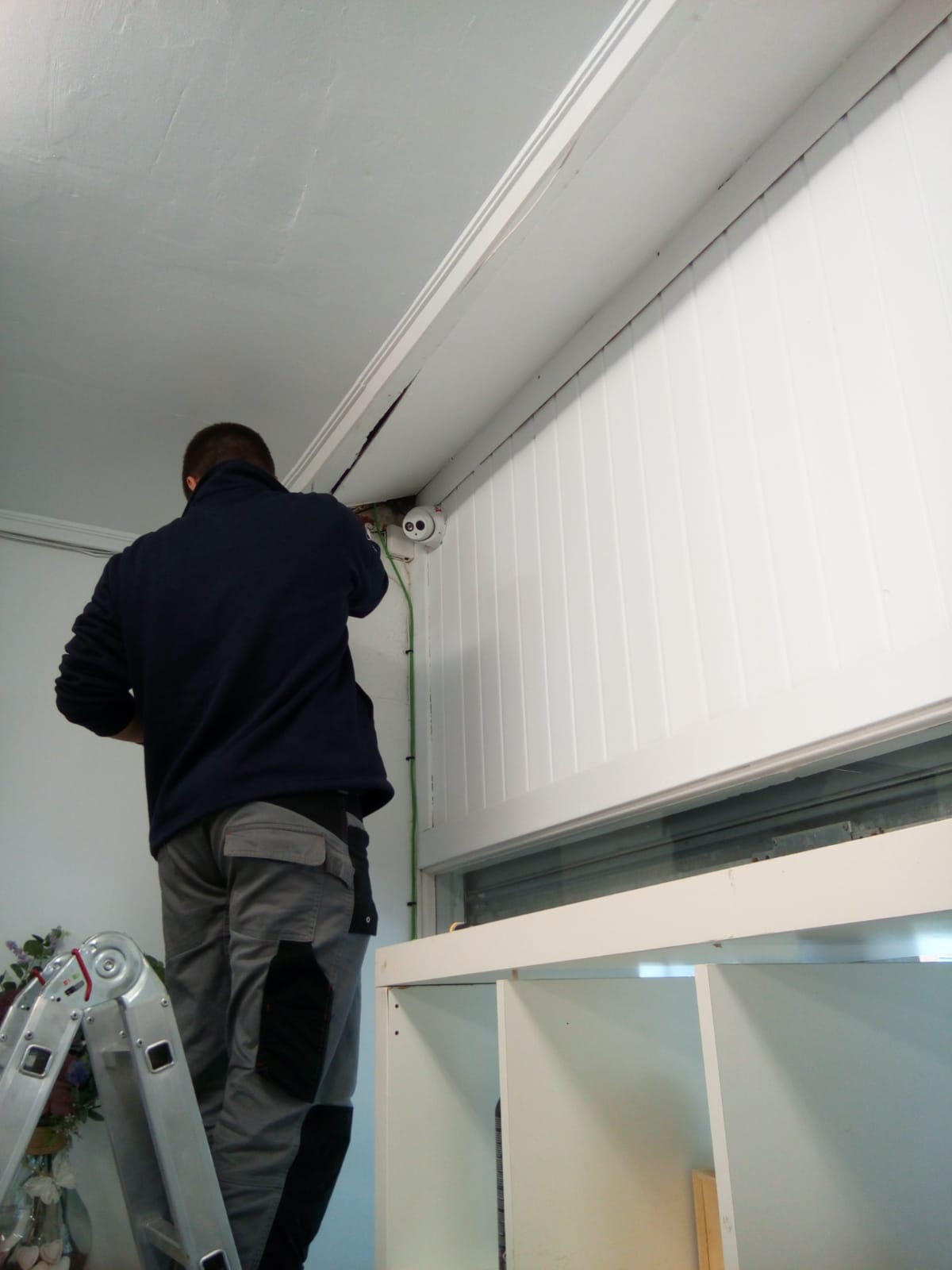
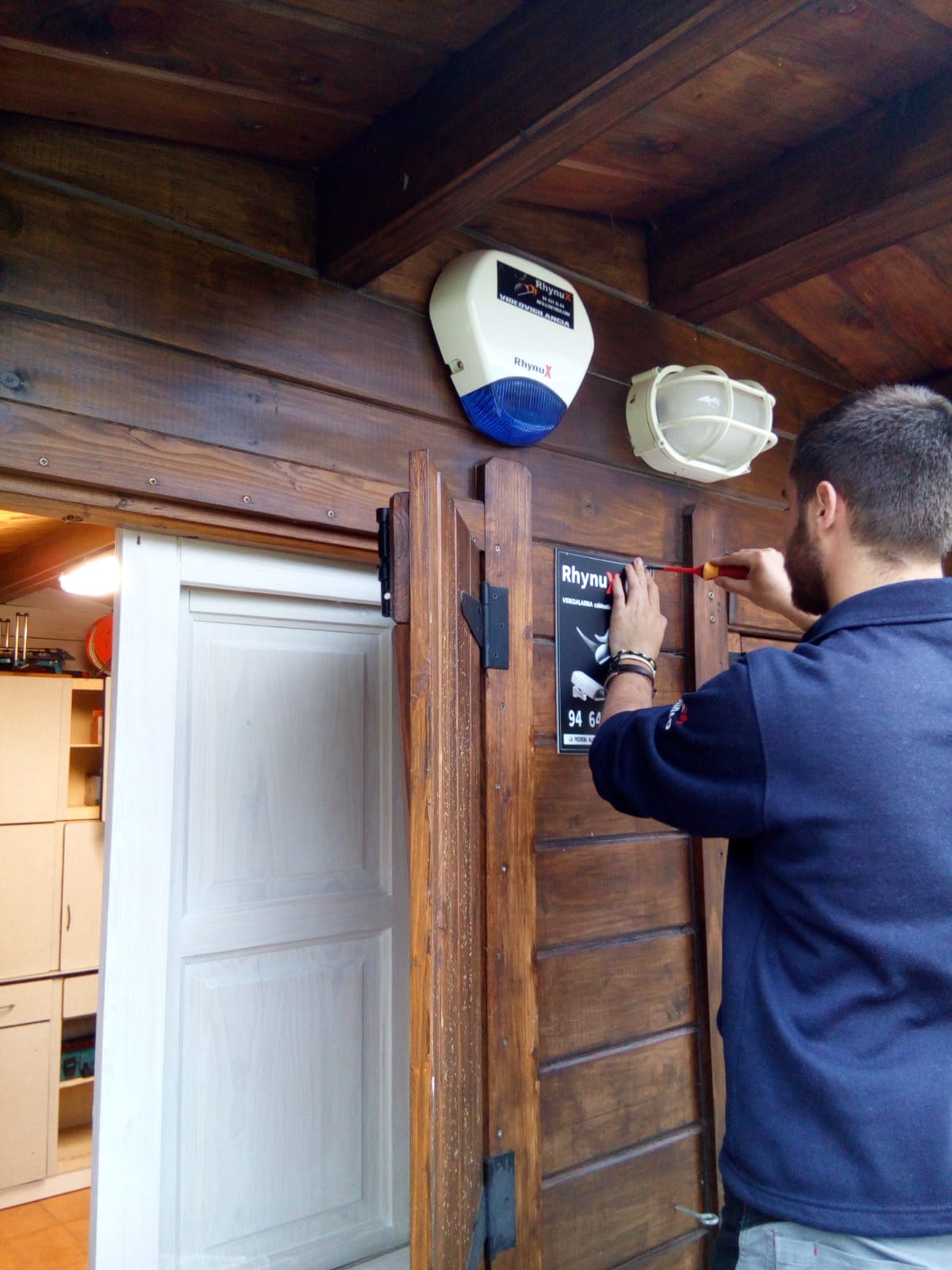








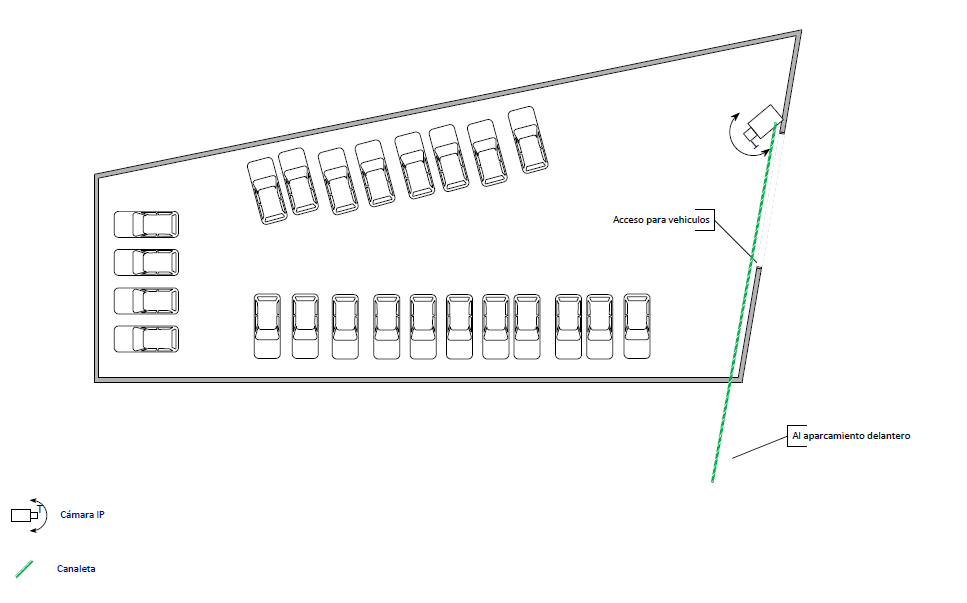
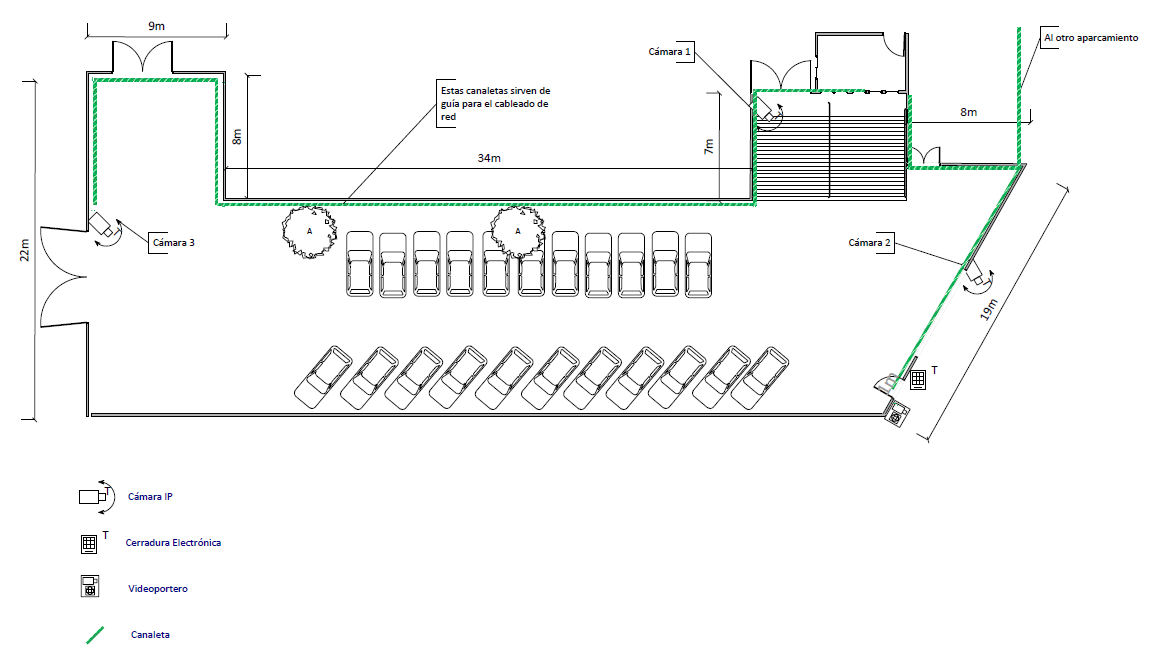

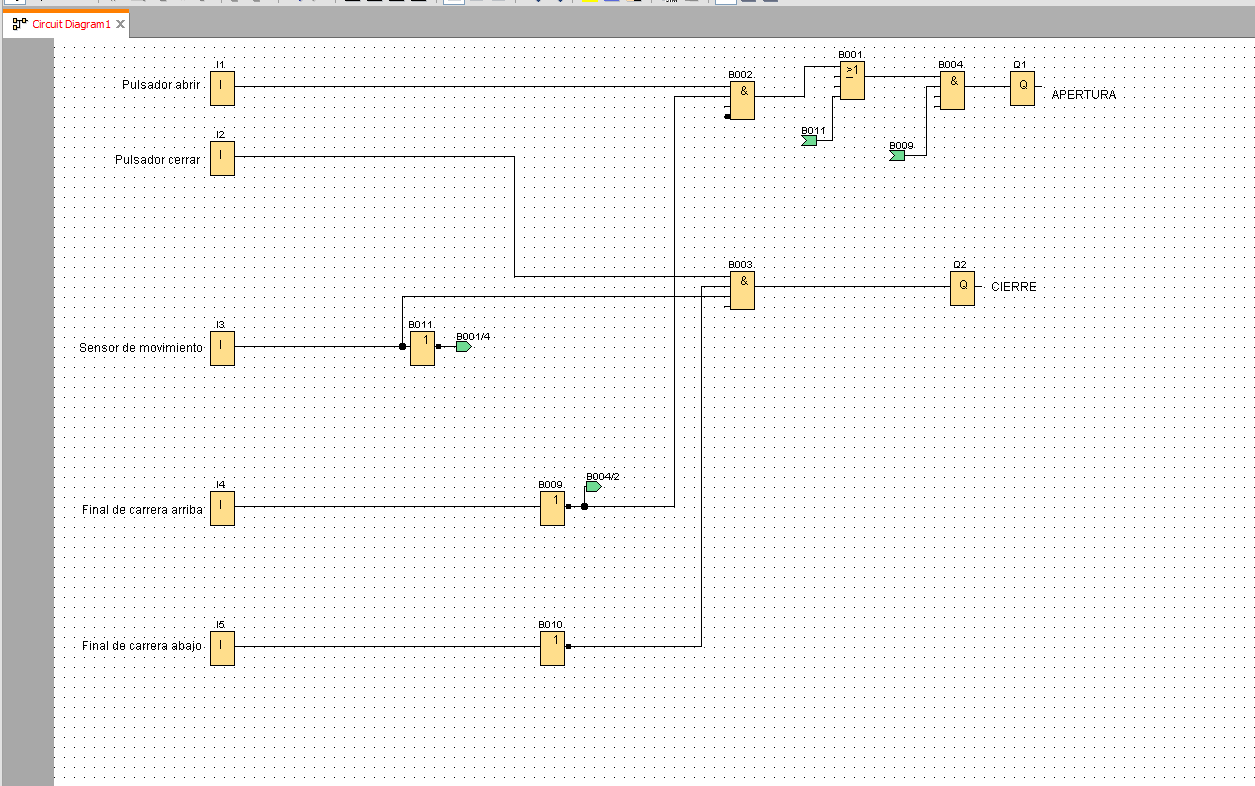



 El cliente se puso en contacto con nuestra empresa porque estaba interesado en domotizar su vivienda. Con intención de realizar un ahorro energético y ganar en seguridad y confort. Además al cliente le interesa poder gestionar su hogar remotamente ya que no pasa mucho tiempo en su domicilio.
El cliente se puso en contacto con nuestra empresa porque estaba interesado en domotizar su vivienda. Con intención de realizar un ahorro energético y ganar en seguridad y confort. Además al cliente le interesa poder gestionar su hogar remotamente ya que no pasa mucho tiempo en su domicilio.